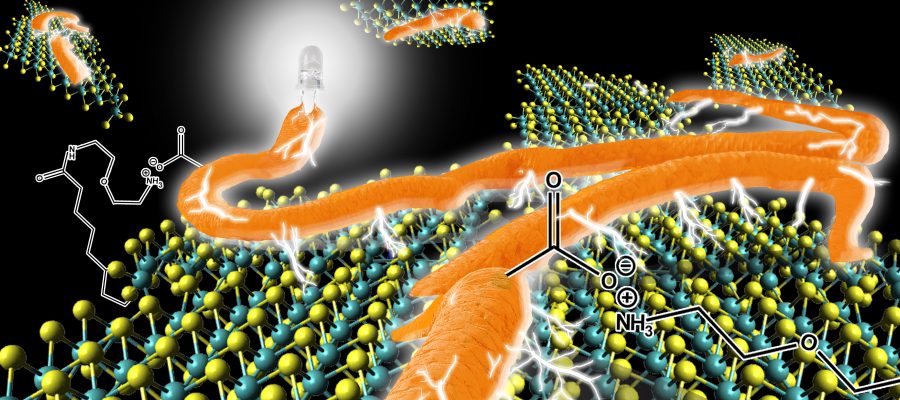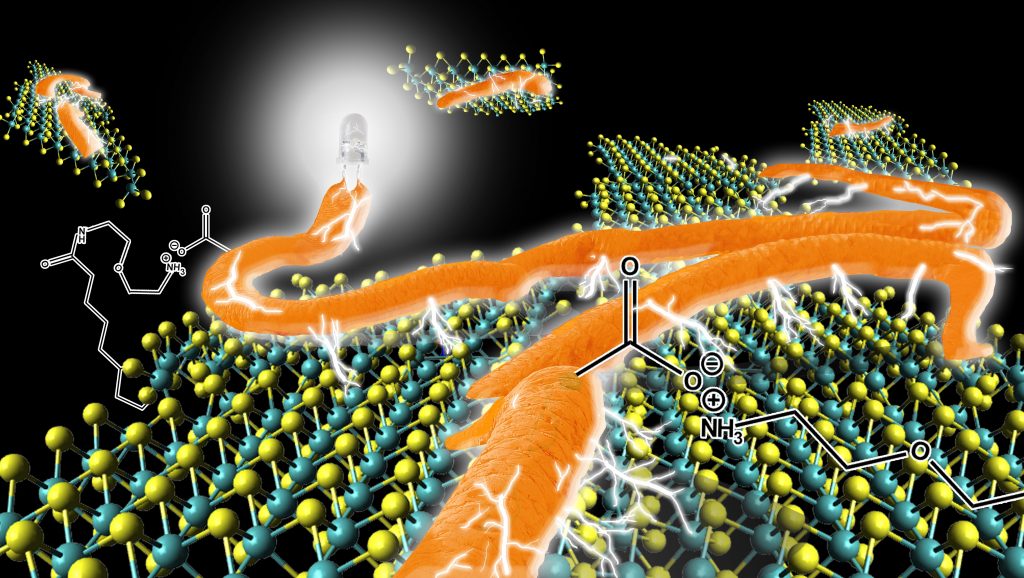
Graphene is a 2D nanomaterial with semi-metallic character, due to its high conductivity and its thickness of only one carbon atom, it has great use in nanotechnology. The TMDs, like the MoS2 or WS2, are similar to graphene, but with a semiconductor character. They are also 2D materials with a thickness less than one nanometer and with a great capacity to give and absorb electrons, being of great interest in the development of new solar panels. However, TMDs have no affinity with other species necessary to increase the conversion of light into electricity. In this article, the authors incorporate species with positive charges (protonated amines) to bring a conductive polymer (polythiophene) with negative charges (carboxylates) approaching the two species through electrostatic forces. The new material proved to enhance the conversion of light into electricity. Advancing towards a more sustainable future.
That´s what we see en our last ACS publication